In today’s digital landscape, a reliable backup strategy is not just a best practice—it’s essential. Data loss can be catastrophic: according to studies, 60% of companies that suffer major data loss shut down within six months. The 3-2-1 backup strategy, widely adopted for its simplicity and effectiveness, provides a robust solution for safeguarding your data against threats such as ransomware, human error, and system failures.
What Is the 3-2-1 Backup Strategy?
The 3-2-1 rule was originally proposed by photographer Peter Krogh as part of his digital workflow. It’s now considered a gold standard in IT environments.
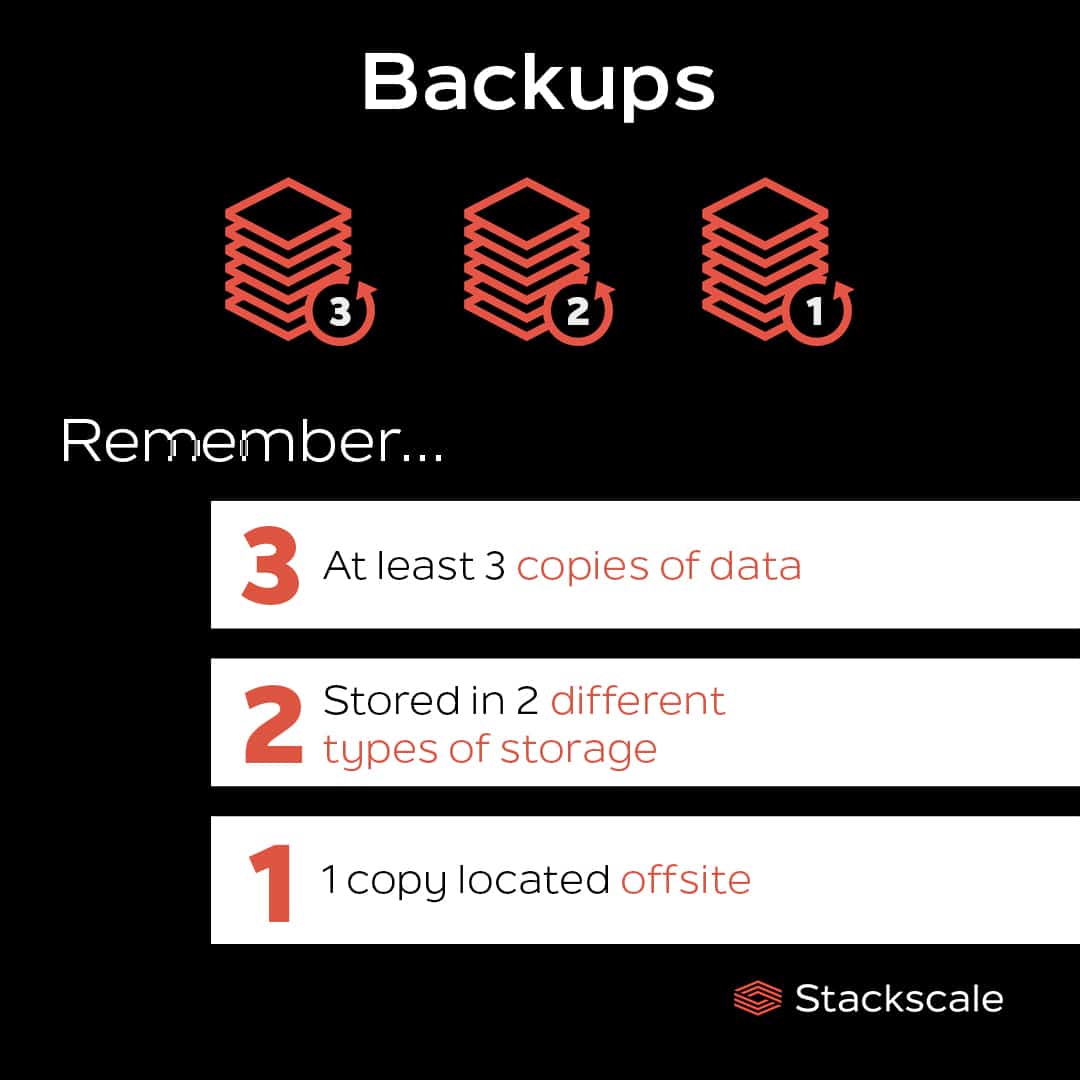
The 3-2-1 rule means:
- 3 copies of your data: One primary copy and at least two backups.
- 2 different types of storage media: Such as a local NAS and cloud storage, or an internal hard drive and an external drive.
- 1 off-site copy: A backup stored in a different physical location or data center.
This approach ensures redundancy, minimizes risk, and improves recoverability in case of incidents.
How to Implement the 3-2-1 Strategy
1. Select the Right Backup Media
Using at least two different storage media is key. Some of the most commonly used include:
- Internal or external hard drives – Good for local storage but may have limited durability.
- NAS (Network Attached Storage) – Centralized storage accessible by multiple systems.
- Cloud storage – Scalable and accessible remotely, though data privacy and cost should be considered.
- Data centers or colocation – Ideal for secure, off-site backups with physical separation from the main site.
2. Configure Local and Off-Site Backups
Make sure backups are spread across different locations:
- Store one copy locally, such as on an internal server or on-premises NAS.
- Store at least one backup off-site—for example, in a private cloud or a dedicated server in a geographically remote Stackscale data center.
- This protects against localized threats like natural disasters, hardware failure, or cyberattacks.
3. Choose and Install Backup Software
The backup software you select should support:
- Automation – To streamline backup creation and reduce errors.
- Scheduling – To ensure regular backups (daily, weekly, etc.).
- Versioning – Keeping multiple versions of files for easy recovery.
- Encryption – To protect sensitive information.
- Compression – To optimize storage space.
4. Automate and Schedule Backups
Backups should be scheduled regularly based on your data’s criticality and compliance requirements (e.g., GDPR or sector-specific mandates). For example:
- Daily backups for sensitive customer or financial data.
- Weekly or monthly backups for less volatile information.
Modern backup solutions support full automation, helping ensure consistency without requiring daily manual intervention.
5. Validate Backup Integrity and Test Recovery
Don’t wait until disaster strikes to find out your backups don’t work. Implement the following:
- Run periodic test restores to confirm files are intact and accessible.
- Simulate real-world recovery scenarios to test speed and efficiency.
- Use checksum tools (e.g., MD5, SHA256) to verify data consistency.
Advantages of the 3-2-1 Strategy
- Data loss protection – With redundant backups in different formats and locations.
- Reduced downtime – Faster recovery after data loss or cyber incidents.
- Ransomware resilience – Off-site or disconnected backups prevent attackers from encrypting all copies.
- Regulatory compliance – Helps meet data protection mandates like GDPR, ISO 27001, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
- Scalability – Adapts to growing data volumes and evolving business needs.
Going Further: The 3-2-1-1-0 Rule
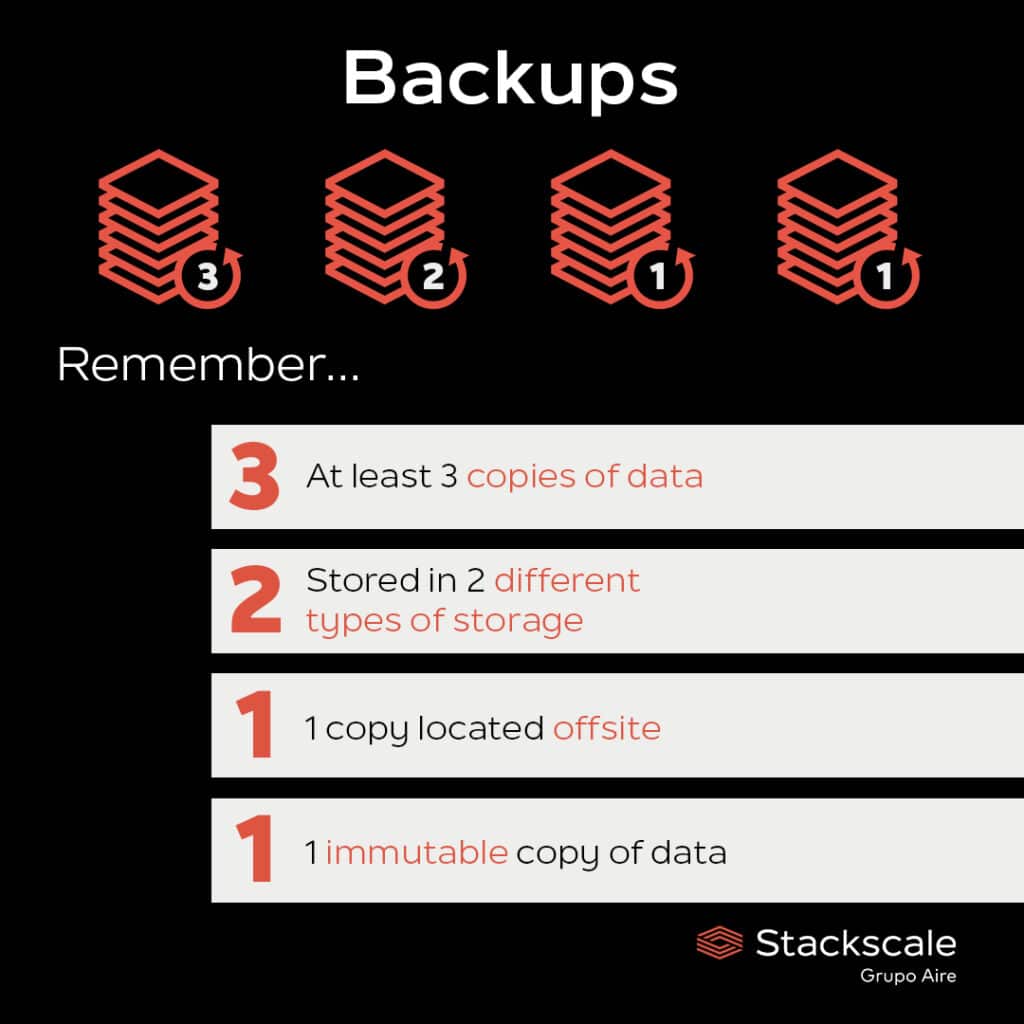
Some organizations adopt an enhanced version of this strategy for added security:
- 3 copies of data.
- 2 types of storage media.
- 1 off-site copy.
- 1 offline or immutable copy (e.g., air-gapped).
- 0 backup errors, verified through regular testing.
This advanced strategy protects against sophisticated threats, ensuring one backup remains untouched by malware or system breaches.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Implementation costs vary depending on the tools and infrastructure chosen. Stackscale offers private cloud and bare-metal server environments that support flexible backup strategies, optimized for cost-efficiency and compliance.
Unlike public cloud providers, Stackscale avoids hidden fees such as egress charges, helping businesses maintain predictable costs over time.
Conclusion
The 3-2-1 backup strategy is a simple yet powerful approach to business continuity. It offers a solid foundation for any organization looking to reduce the risk of data loss, ensure compliance, and improve disaster recovery readiness.
At Stackscale, we help companies implement tailored backup strategies using high-availability private cloud infrastructure and bare-metal servers hosted in Europe, ensuring total data control and privacy.
Ready to strengthen your backup plan? Contact our team and discover the ideal backup solution for your business.